Carl R. Woese Institute for Genomic Biology
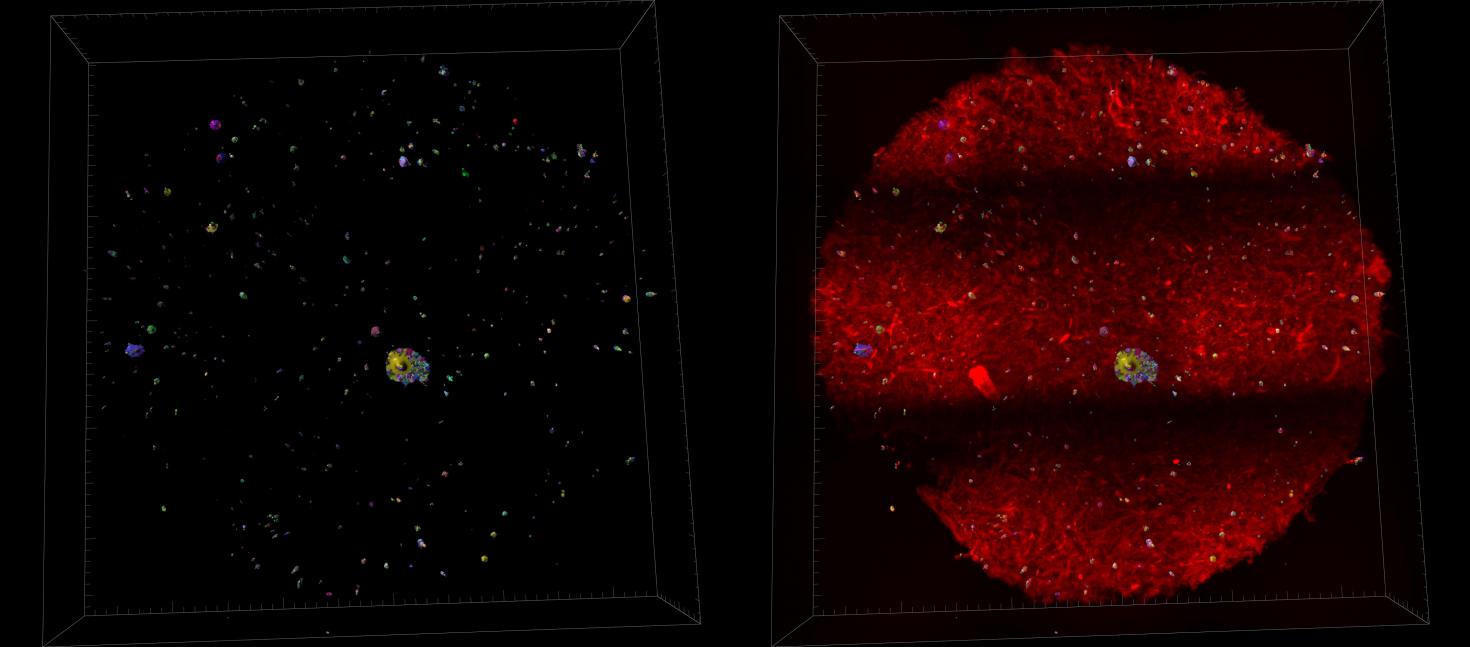

Towards the development of a fast and robust protocol for the clearing and imaging of Mineralized Collagen Scaffold, embedded with cells. A secondary goal is adopt the protocol for a high throughput clearing and imaging samples on a large scale.
Instrument: Imaged with Miltenyi Utramiscrocope and processed with Imaris 3D Software

This crown root from biomass sorghum grown in the field under restricted water supply using our rain-out facility as part of the CABBI project. This Image was taken using the X5000 NSI High-Resolution Micro-CT and rendered in Imaris at the Carl R. Woese Institute for Genomic Biology Core facility.


These images depict a slice of a coal ball from the Pennsylvanian period (~300 million years ago), that contains permineralized plant material from a peat swamp. CT allows us to distinguish the plant organs contained within a coal ball for taxonomic identification. The images were taken using an X5000 NSI High-Resolution Micro-CT and rendered in Imaris at the Carl R. Woese Institute at the Genomic Biology Core Facility.
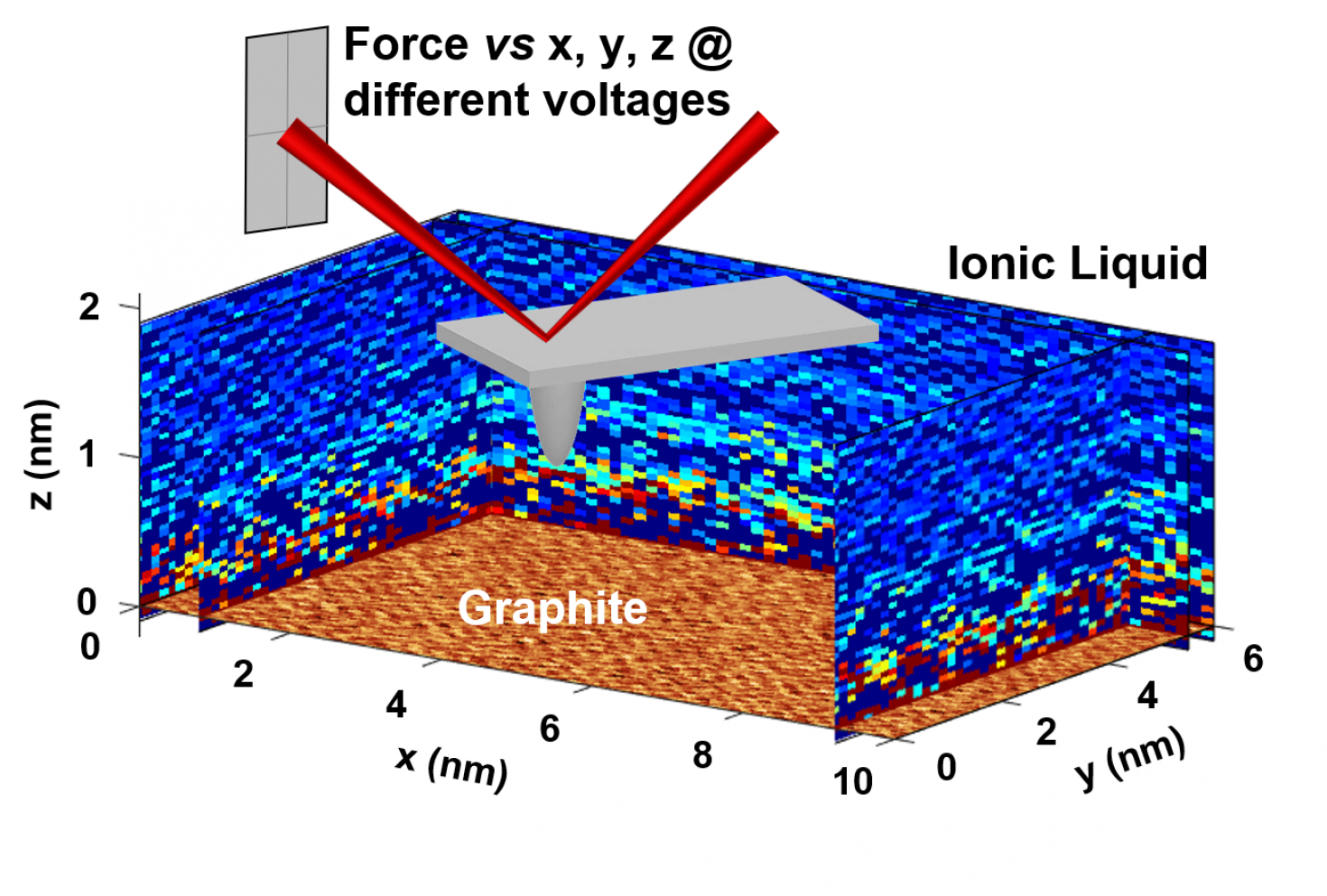

Molecular-scale structure of the electric double layer at the interface of an ionic liquid and graphite, imaged for the first time with a technique developed by the Zhang research group and the Cypher AFM in the IGB Core. Work published in ACS Nano 2020, 14, 17515−17523.
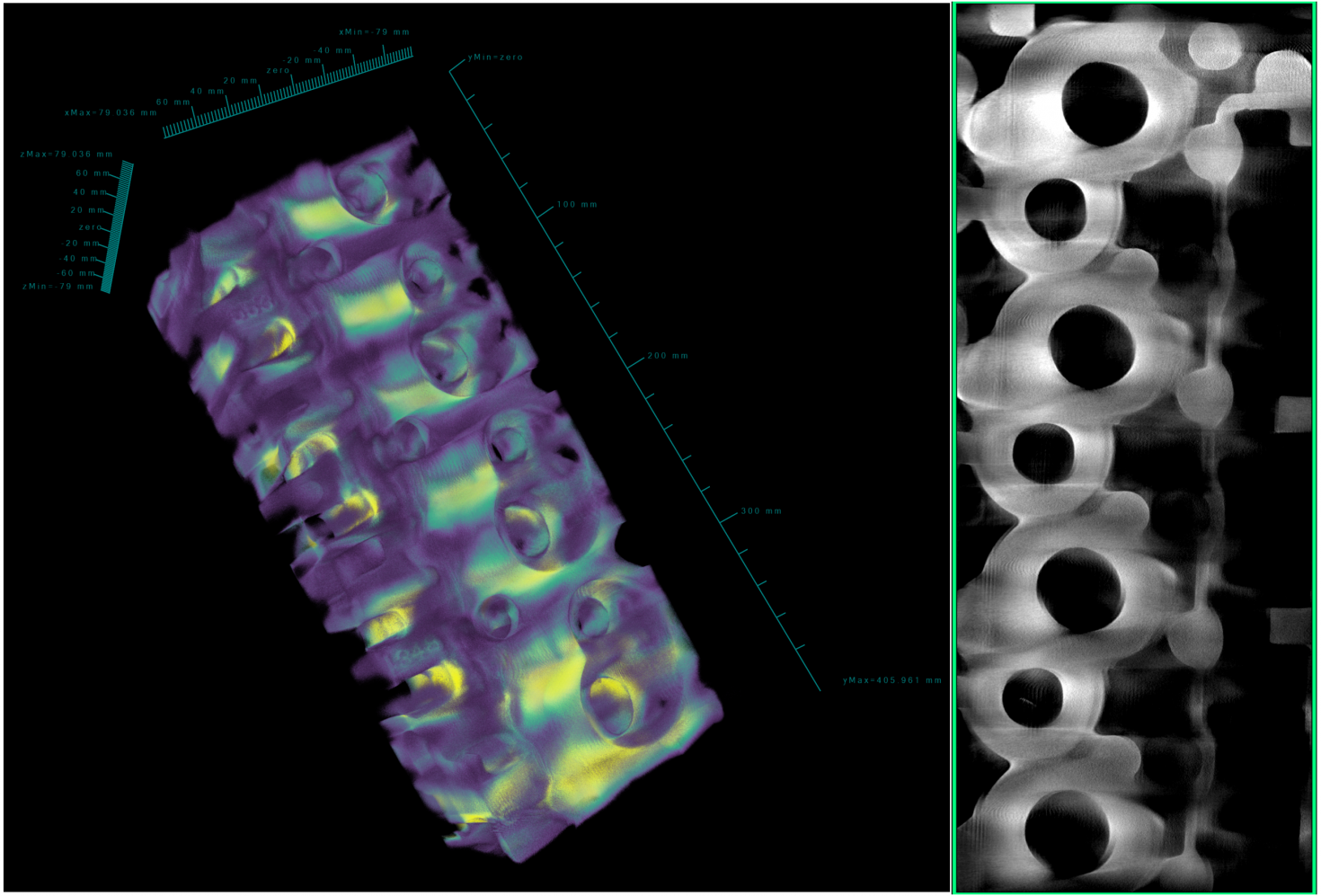
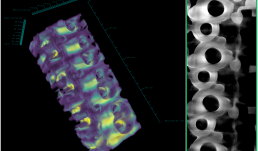
The image shows the 3D CT reconstruction of a high performance cylinder head cast from scrap aerospace aluminum alloy AA7075. This helps in determining casting defects such as, microporosity and hot tearing. The cylinder head measures 20x8x5.75 inches and weighs approximately 40 pounds. The 3D images were obtained using the NSI X-5000 3D micro CT system and rendered using NSI efX software at the Carl R. Woese Institute for Genomic Biology Core Facility.
“This material is based upon work supported by the U.S. Department of Energy’s Office of Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy (EERE) under the Advanced Manufacturing Office Award Number DE-EE0007897 awarded to the REMADE Institute, a division of Sustainable Manufacturing Innovation Alliance Corp”.
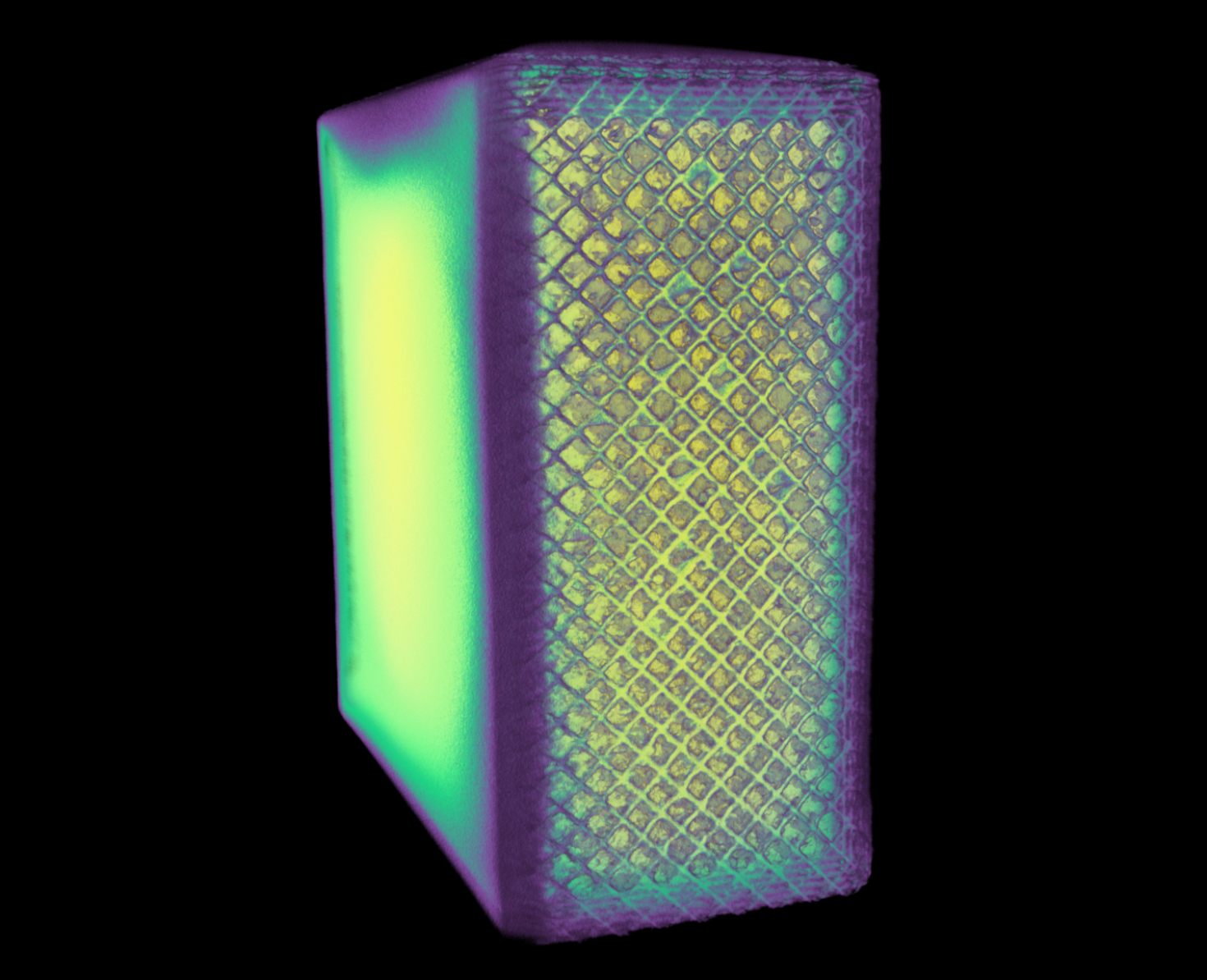

The image shows the density of 1x2x2 cm^3 cube of a manufactured 316 stainless steel block using selective laser sintering (a 3D-printing process). The CT scan helps in determining defects produced in the material during the manufacturing process. This was scanned using the NSI X-5000 3D micro CT system and rendered using NSI efX software at the Carl R. Woese Institute for Genomic Biology Core Facility.
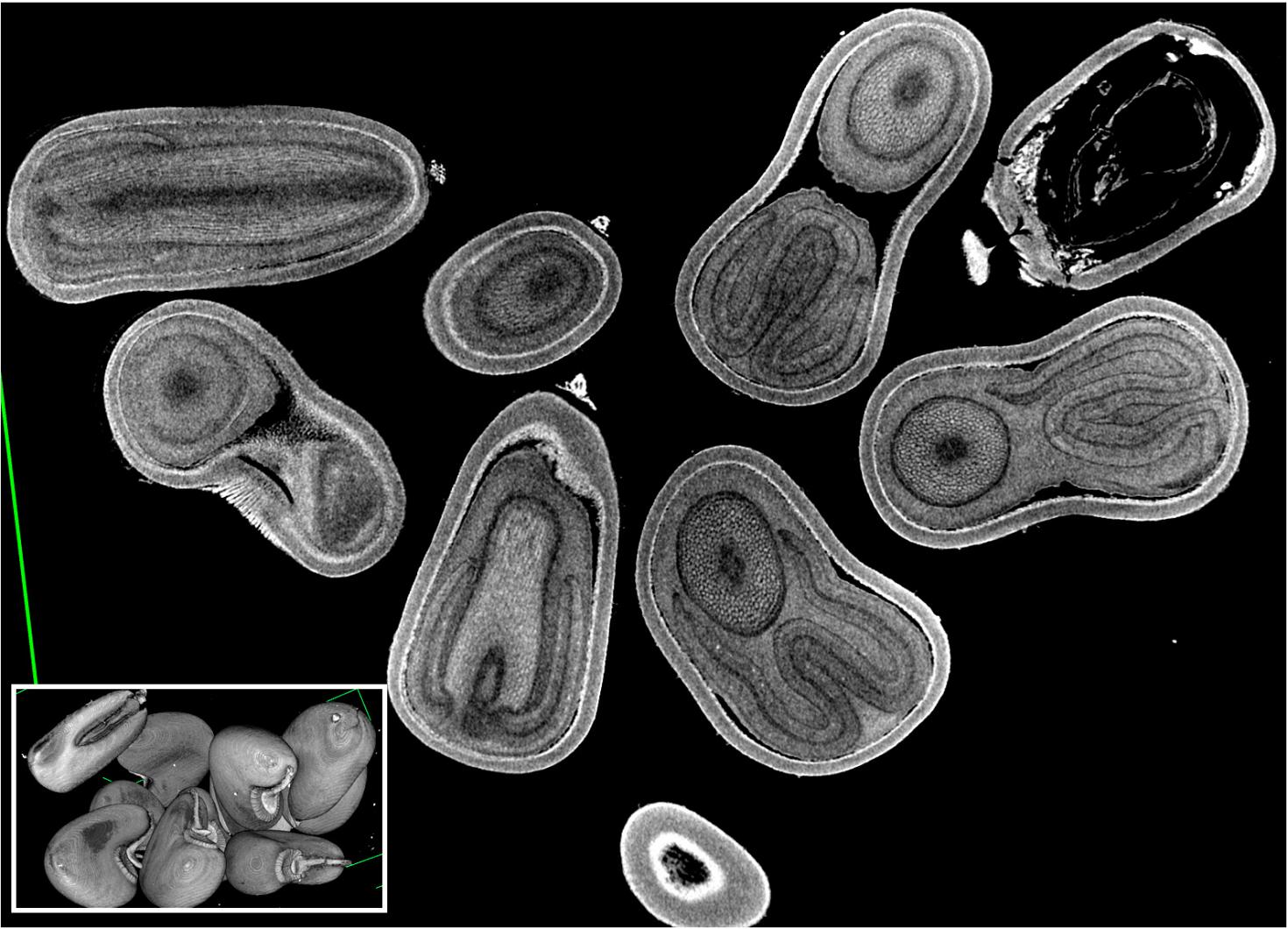

The image is showing a 2D rendering of both three-dimensional (3D) images of Velvet leaf (Abutilon theophrasti) intact seeds (~ 2-4 mm in diameter, inset) and a single 2D virtual section collected from the UIUC Agricultural Fields in Urbana, IL. It is an invasive species that is considered a damaging weed to agricultural crops, such as corn and soybeans. The images are acquired by the X-5000 micro CT system and rendered in NSI CT software at the Carl R. Woese Institute for Genomic Biology Core Facility.
The image is showing a 2D rendering of three-dimensional (3D) mouse adipose tissue cleared using IDISCO clearing technique and labeled with fluorescent dye against F4/80 protein (a macrophage marker). This fluorescent image was taken with the Ultramicroscope and rendered using the Imaris software at the Carl R. Woese Institute for Genomic Biology Core Facility.


This image is of an inside contour surface of a Heat Exchanger (Condenser) produced by direct metal laser sintering (DMLS). Reconstructed surface contours like this created in Imaris from X5000 Xray CT date, are used to compare the geometrical parameters of the printed object to the design. The sample was scanned using the X5000 NSI High Resolution Micro-CT and rendered in 3D using Imaris at the Carl R. Woese Institute of Genomic Biology Core Facility. Image provided by Kazi Fazle Rabbi from the Nenad Miljkovic Group.
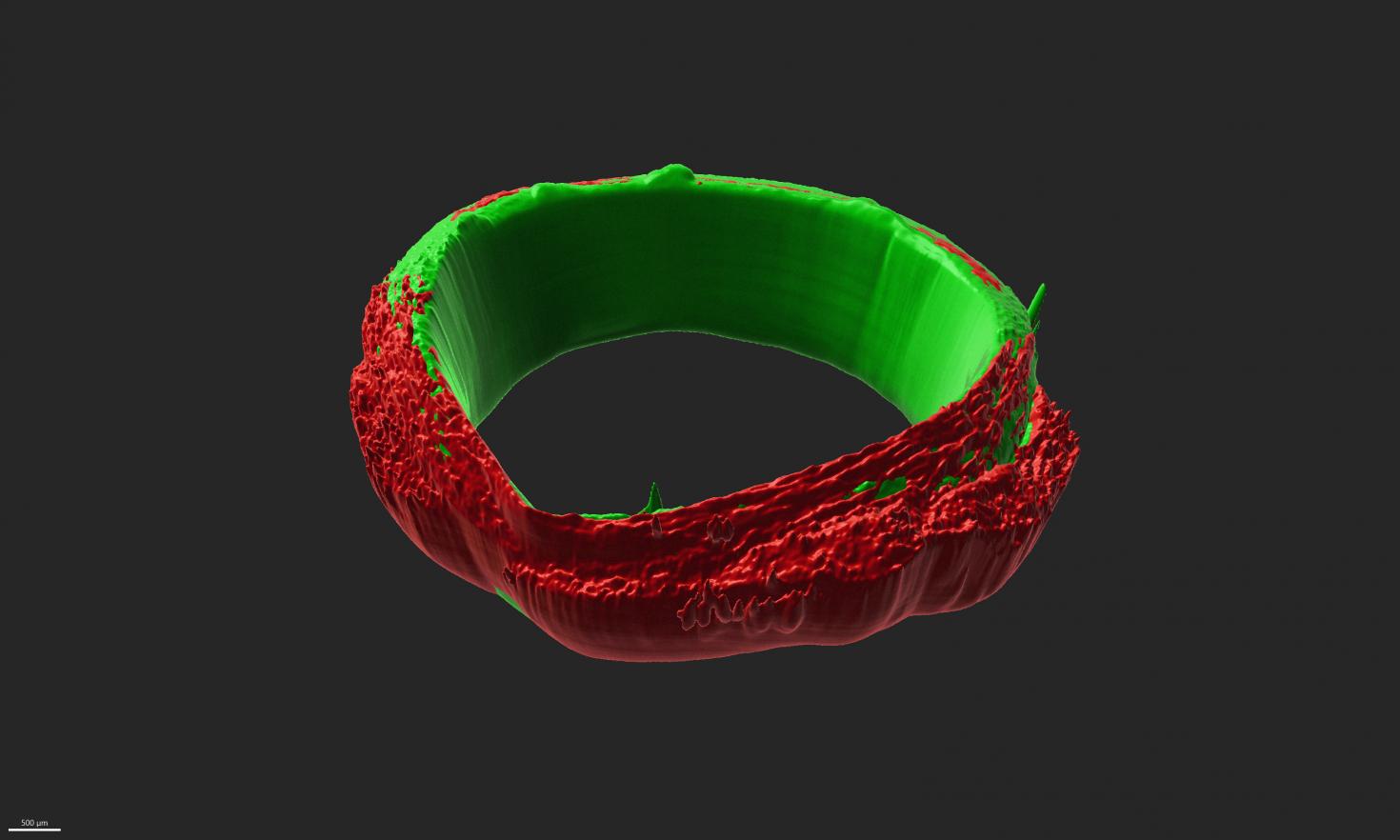

The image is showing engineered three-dimensional (3D) skeletal muscle ring-shaped tissues that are a little under 1mm in thickness, and 6mm in diameter adhered to motor neuron rings of the same dimensions. The image was taken with the Miltenyi Ultramicroscope at the Carl R. Woese Institute for Genomic Biology Core Facility and 3D-rendered using Imaris Software.

View Gallery
1
/
10
