Carl R. Woese Institute for Genomic Biology
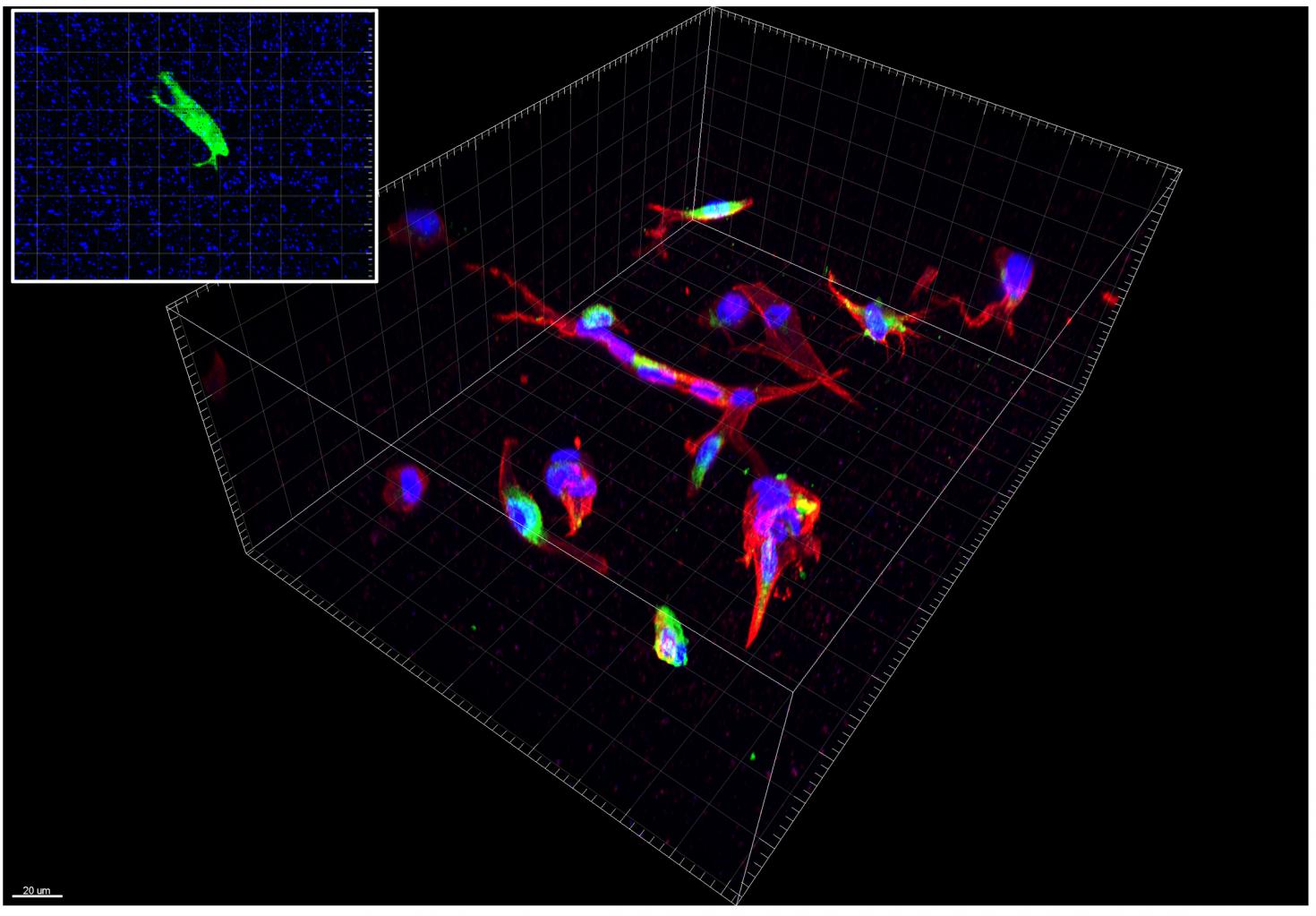
Primary Human hepatic stellate cells cultured in synthetic polyethylene glycol gels with RGD for 5 days. Red: phalloidin actin stain. Green: antibody collagen stain. Blue: DAPI nucleus stain. Inset shows calcein-stained hepatic stellate cell (green) encapsulated in a synthetic polyethylene glycol gel embedded with fluorescent beads (blue). A healthy cell’s cytoskeleton is depolymerized using Cytochalasin D. Change in bead position is captured and analyzed along with the gel’s stiffness to calculate the three-dimensional traction force of the cell using Imaris software. System Zeiss LSM 880 with Imaris Software.

Tissues from mouse medial prefrontal cortex were cleared by CLARITY and stained with anti-proteolipid protein. Images were taken on the LSM 710 and 3D renderings were created using Bitplane Imaris software. This technique allows 3D visualization and quantification of myelin in the prefrontal cortex. Left: maximal demyelination due to cuprizone neurotoxin. Right: partial remyelination one week later.
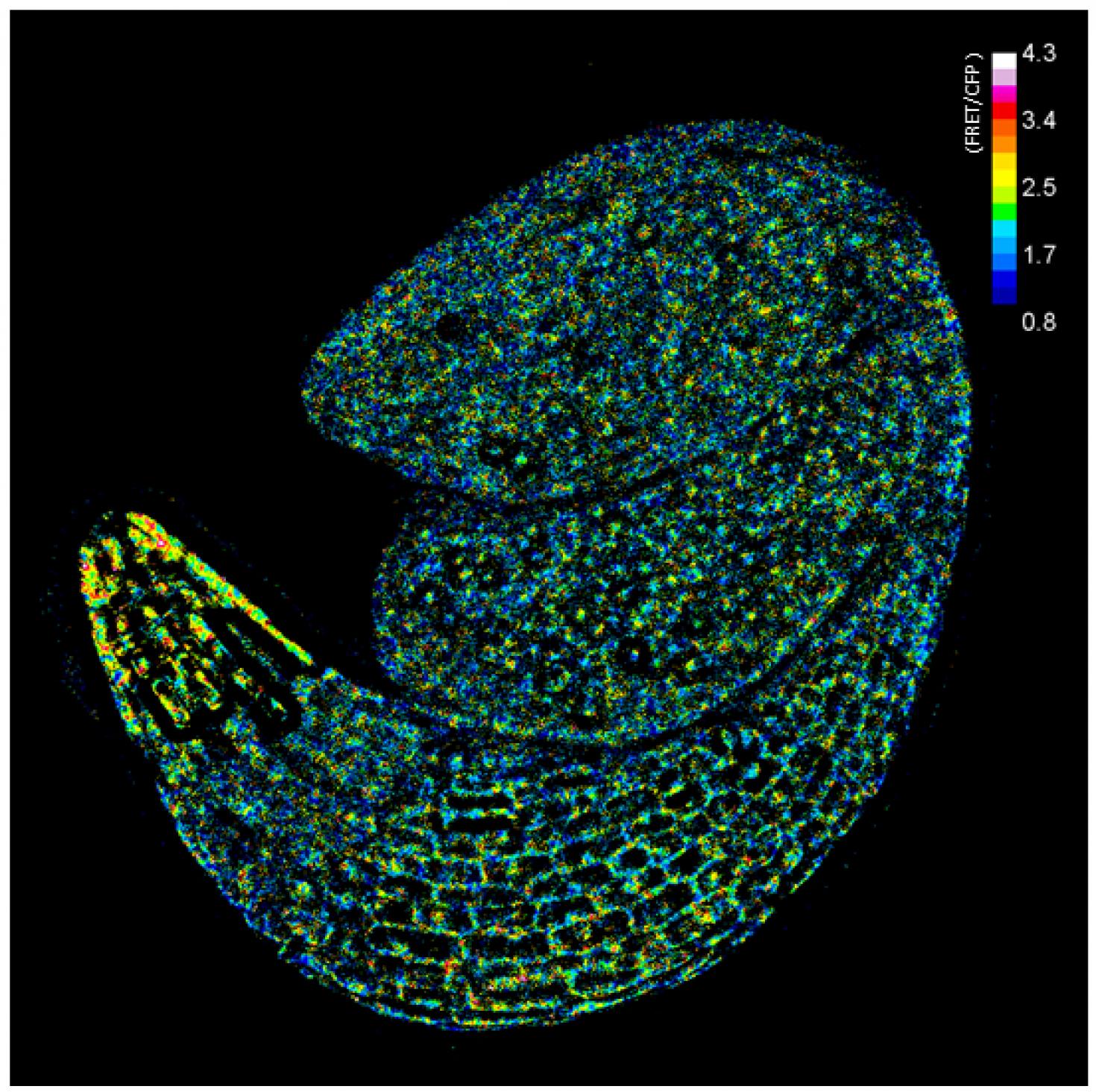
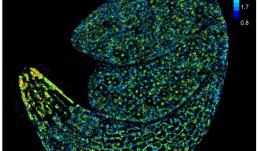
Visualization of glucose distribution in an embryo of Arabidopsis during germination using a FRET glucose sensor.
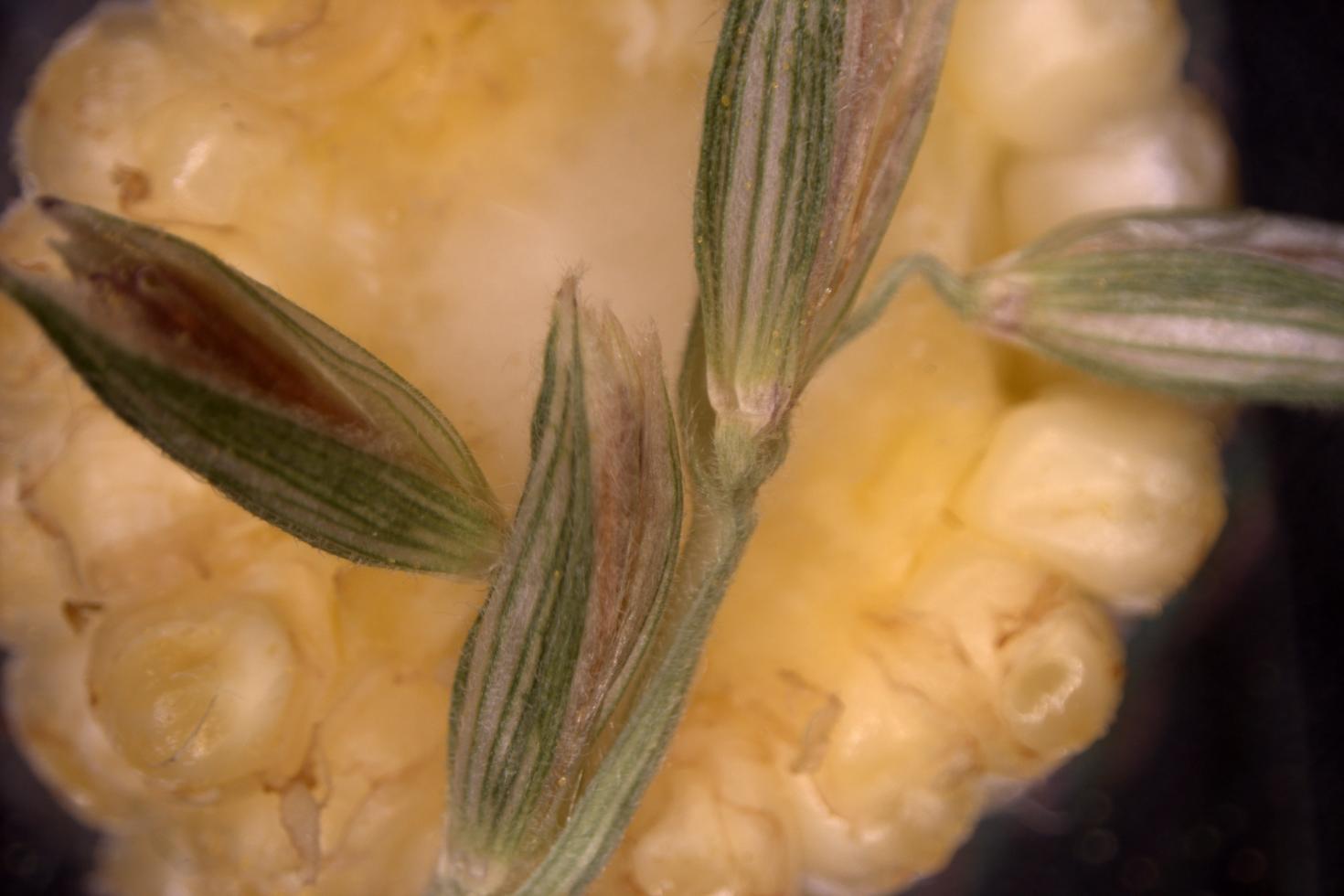


This image is a cross section of a corn cob (behind) and a bunch of spikelets bearing anthers, where the corn pollen is produced. It was imaged on the Zeiss Axioscan V16 with 506 color camera.
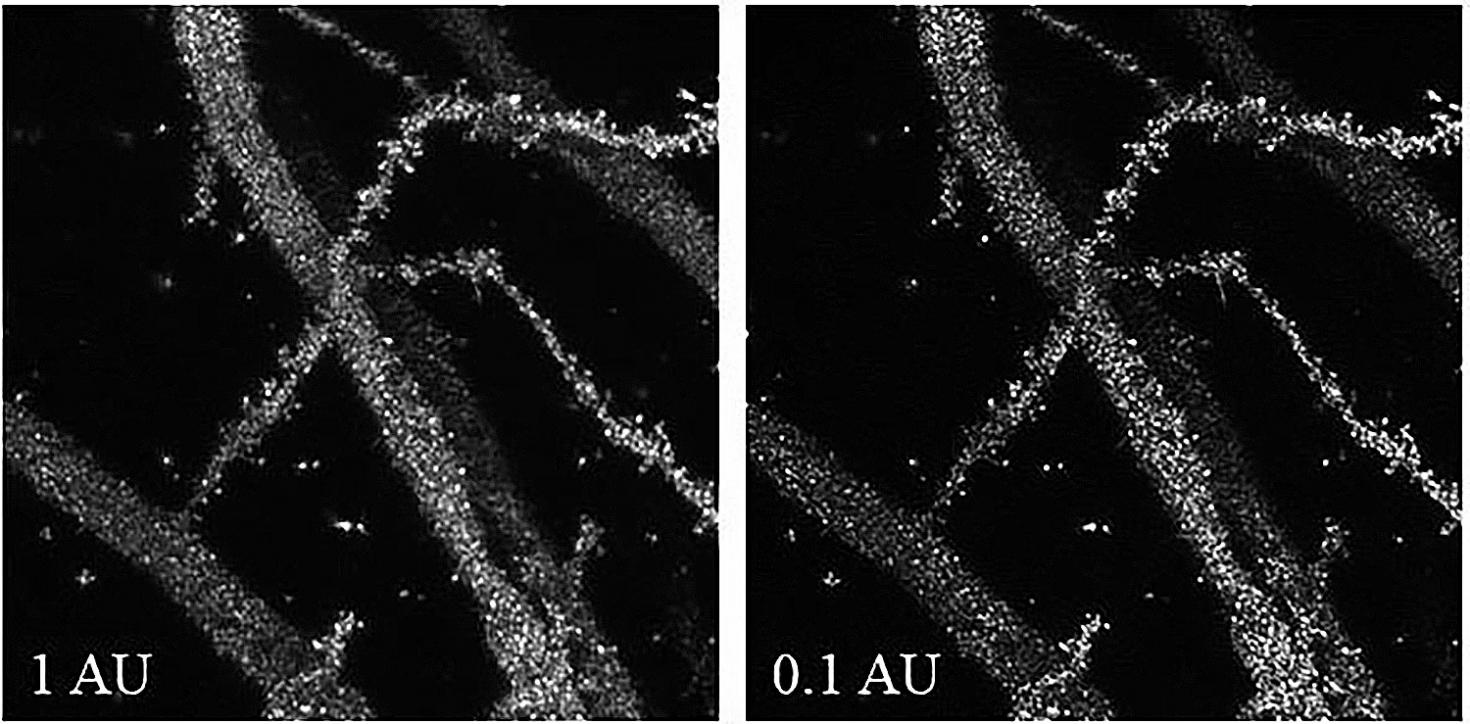
Confocal Reflection Super-Resolution imaging (CRSR) of Golgi-Cox impregnated murine hippocampal neurons taken under the pinhole size condition of 0.1 Area unit (AU) in contrast to the conventional reflection imaging setting at 1 AU. The image was taken with Zeiss LSM 880 with 63x magnification at 3.2 times zoom.
Go to the article: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31237354
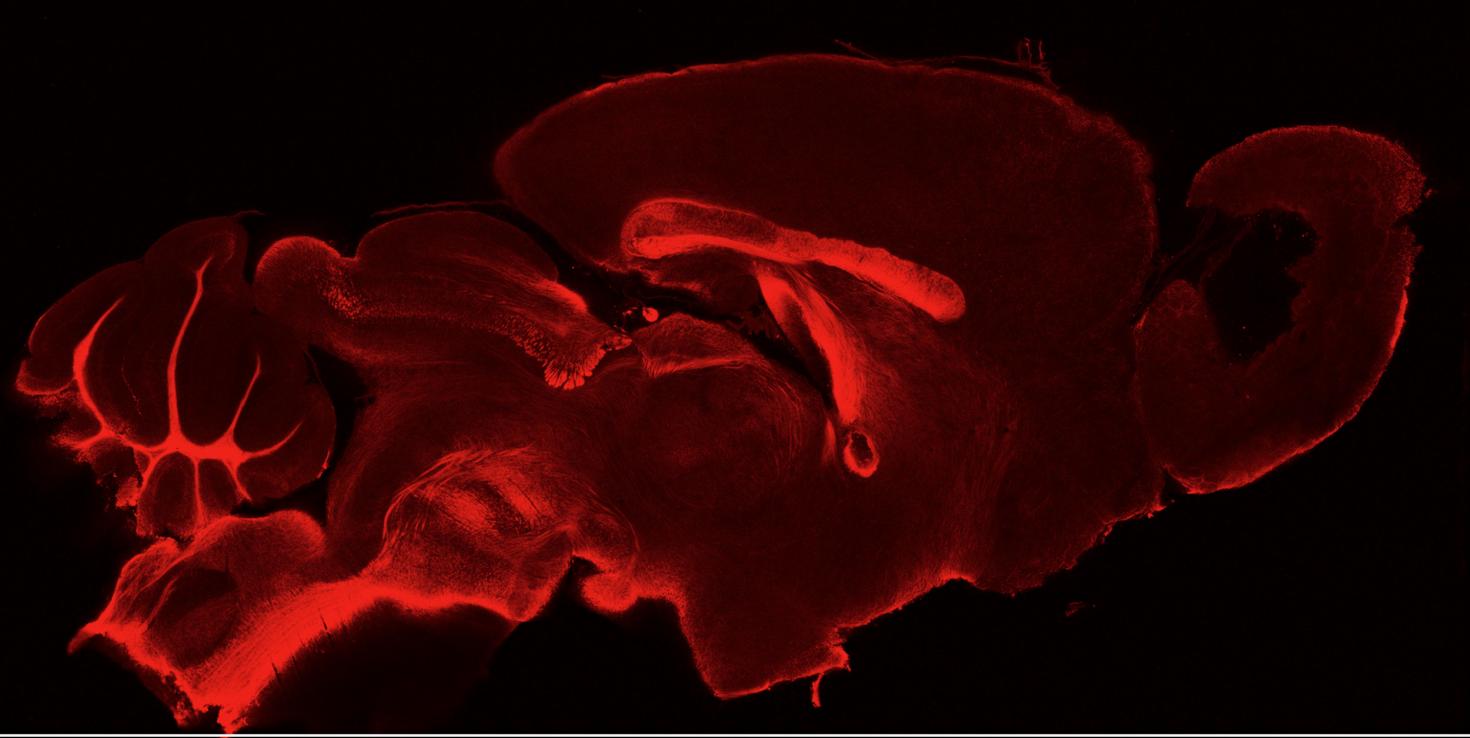

This tile scan of a sagittal brain section of a cuprizone-fed mouse shows characteristic demyelination in the caudal corpus callosum. This mouse was sacrificed during the remyelination phase. The image was obtained with the LSM 710 after CLARITY tissue clearing and subsequent staining with anti-proteolipid protein.
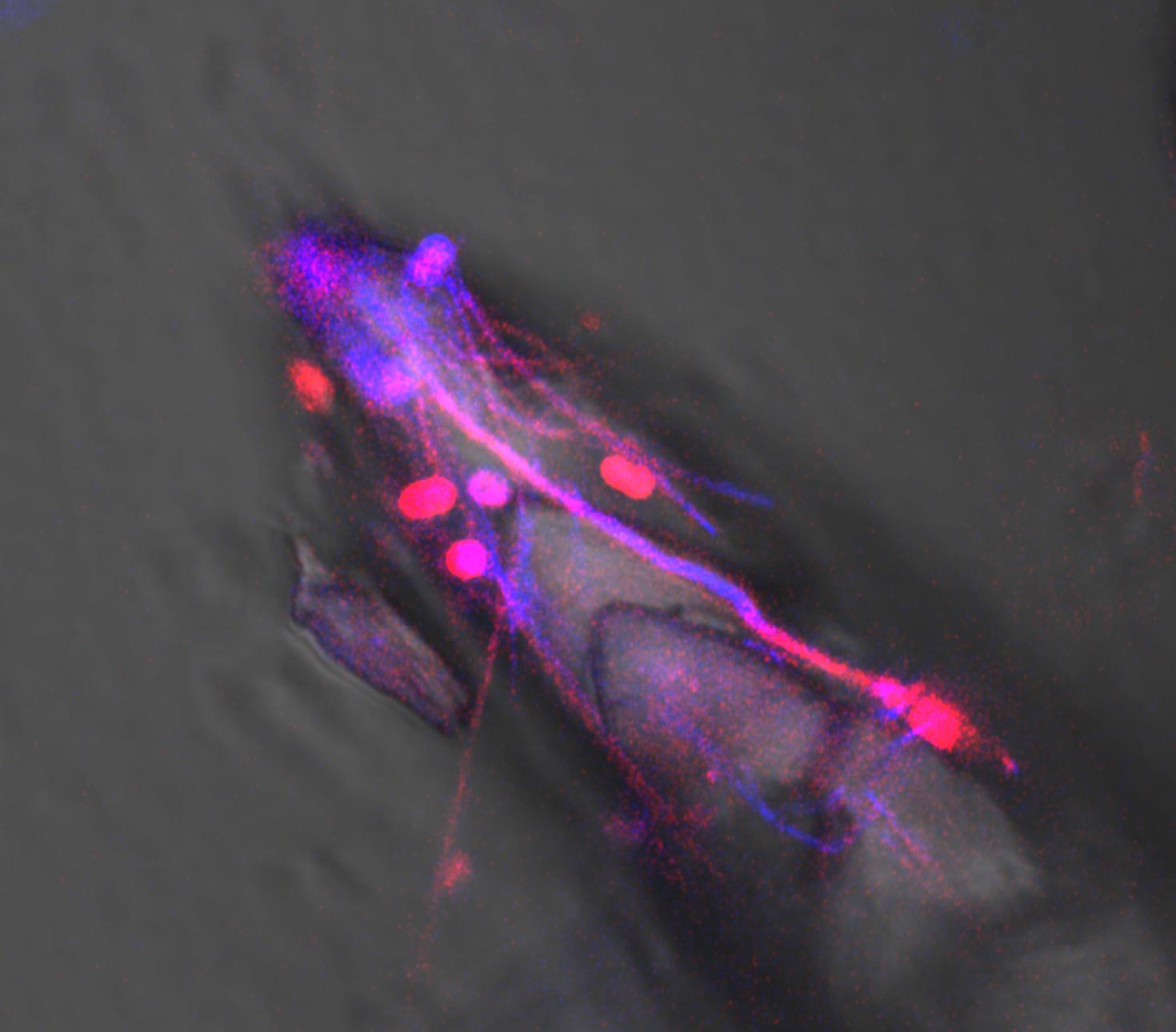
Billion Times Faster: The rate of hot-spring travertine (CaCO3) deposition at Mammoth Hot Springs in Yellowstone National Park is accelerated (catalyzed), reaching crystal growth rates one billion times faster than the rate of CaCO3 deposition in lakes, caves, rivers and oceans around the world. This astonishing rate of precipitation, which amounts to 1 ton of travertine being deposited each day at Mammoth, is driven by the biomolecules produced by heat-loving bacteria (thermophiles) that thrive in the hot springs. This image, which merges transmitted plane-light (brightfield) with Airyscan Superresolution autofluorescence, shows a rapidly extending travertine crystal intimately associated with thermophilic sulfide oxidizing bacterial filaments (Sulfurihydrogenibium yellowstonense) and unknown rod-to-coccoid shaped bacteria.

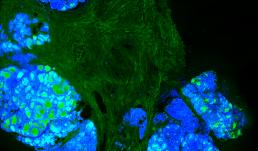
Ductal Network of Bovine Mammary Glands
The image shows bovine mammary gland tissue which is cleared with SWITCH Tissue Clearing technique and immunolabeled with a pan cytokeratin antibody, which labels the entire ductal network. The image was acquired using the Tiling and Stitching Module with the Zeiss LSM 710.
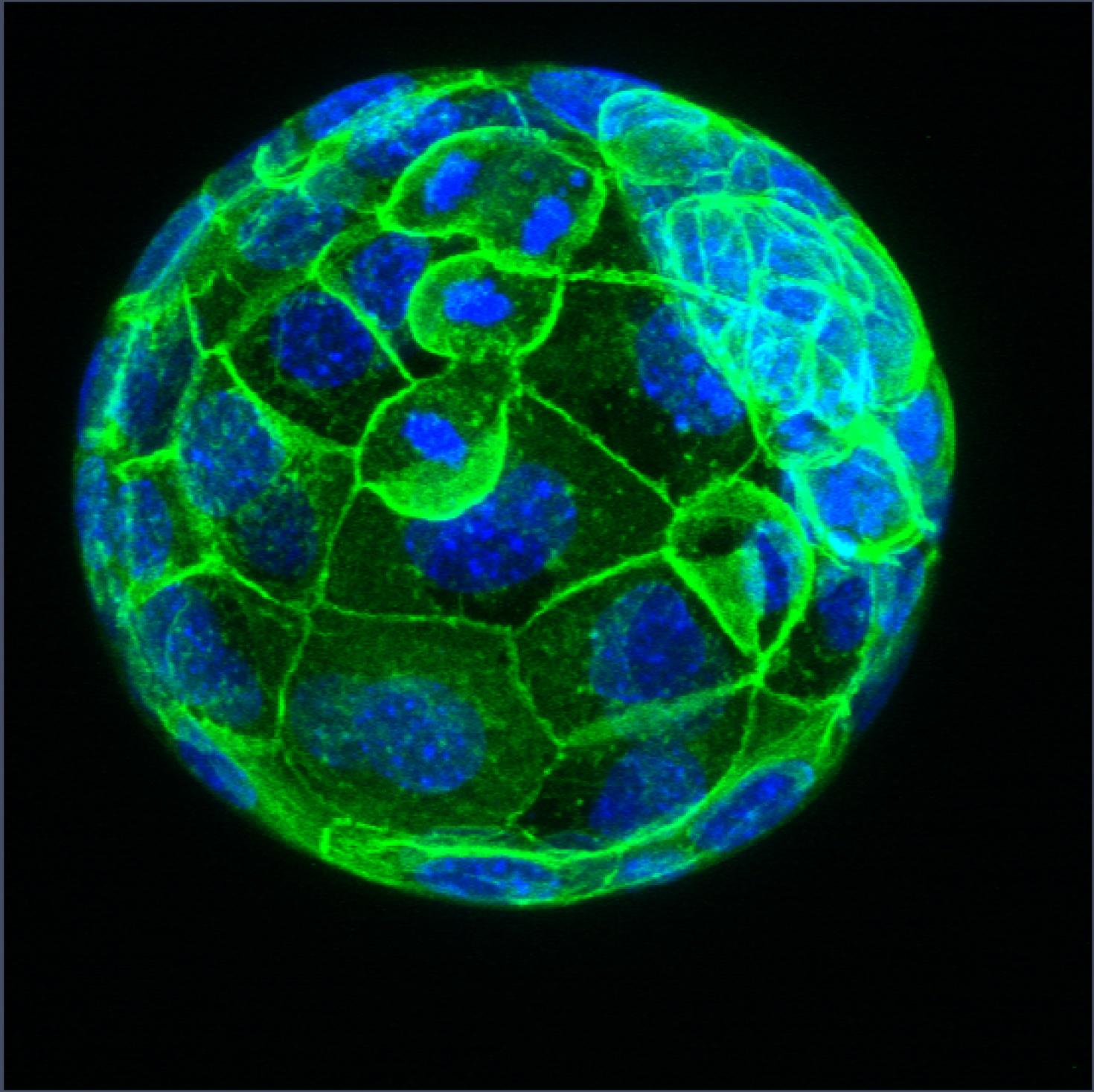
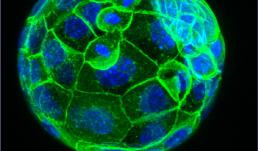
This is an image of a mouse blastocyst exposed to 1µg of a Phthalate mixture. The green color represents E-cadherin expression, a maker for cell adhesion. The blue represents DAPI staining of the nuclei. Phthalates are used in plastic manufacturing to increase flexibility, durability and longevity of plastics. However, phthalates have been identified as endocrine disrupting chemicals that can interfere with normal hormone homeostasis. The aim of this study is to determine whether exposure to relevant phthalate mixture negatively impacts preimplantation embryo development through observation of changes in morphology, cell adhesion and particular proteins in mouse embryos at different stages of development. This project is being conducted by Kadeem A. Richardson, under the supervision of Dr. Romana Nowak of the Reproductive Health and Toxicology Laboratory in the Department of Animal Sciences.


Archaeal cells lacking surface-layer form large clumps with cell size significantly varied. Scale bar: 10µm.

View Gallery
1
/
10
