Carl R. Woese Institute for Genomic Biology
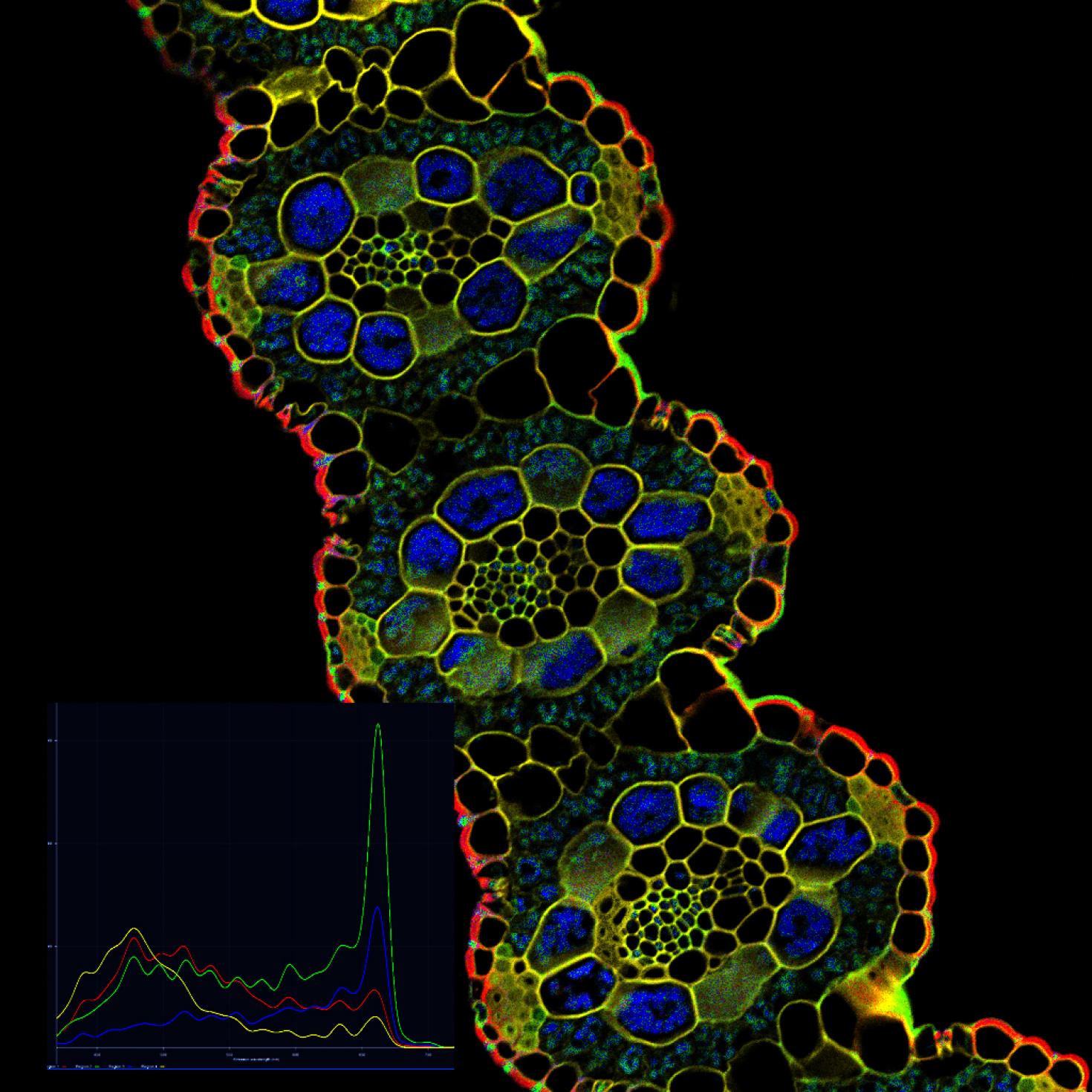
Image showing spectral detection and un-mixing of Switch Grass leaf cross section. System LSM 710 Two-photon System

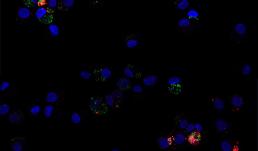
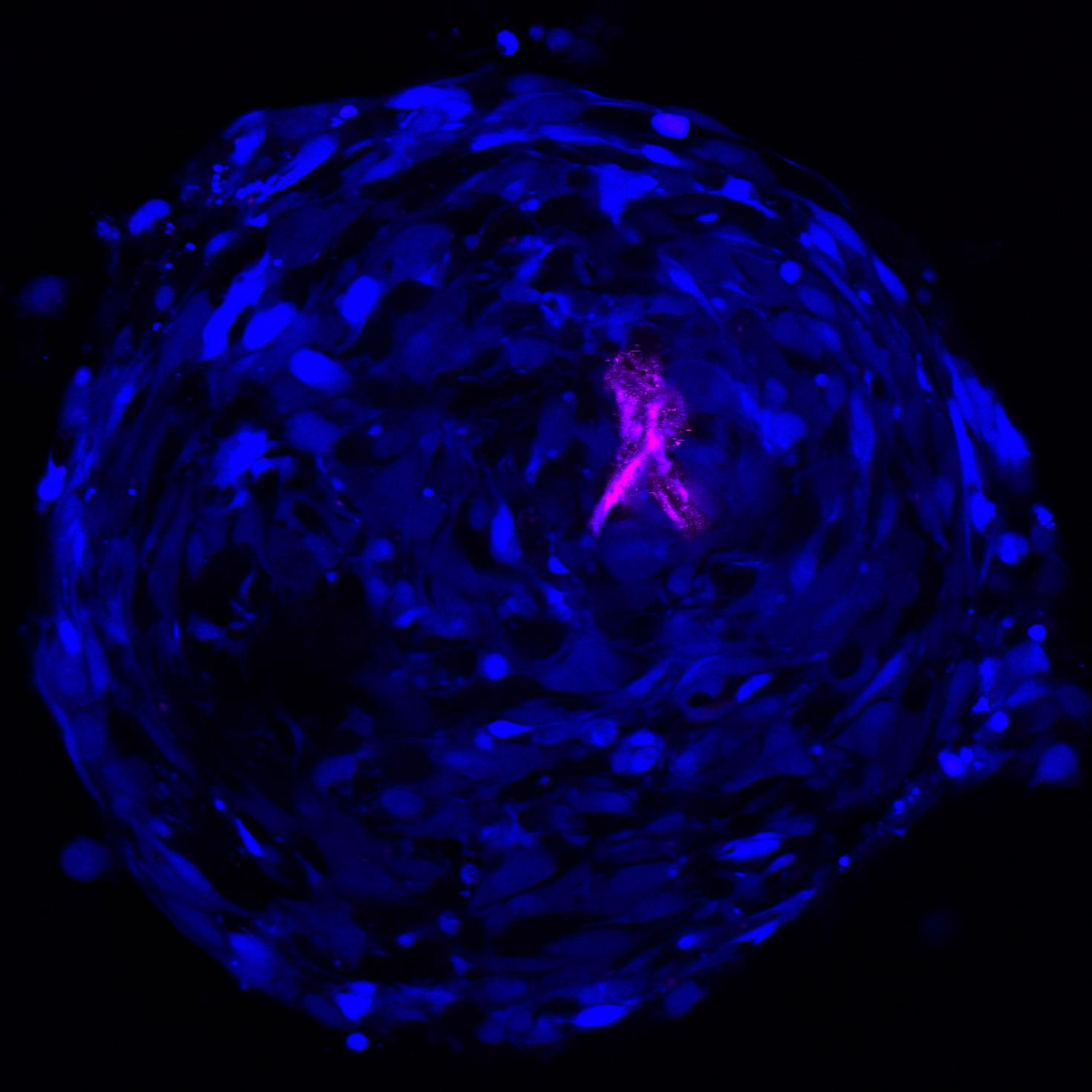
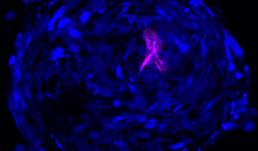
The image depicts human macrophages infected with Yersinia pestis Kim 5 (plague) 10:1 after 24 hours. Here DNA is blue, Y. pestis is green and bacterial death is marked in red. Prepared and visualized by Katie Van Etten (UIUC Anthropology, 2017) as part of the Brinkworth Evolutionary Immunology and Genomic lab's research into the evolution of human immune function. Funded by NSF grant BCS-1750675.
Image preparation and photo credit: Katie Van Etten
Others involved in the production of this image: Keaton McClure (MCB, 2019), Priya Bhatt (Anthropology, 2021), Will Widick (Vet Med, 2019), Alex Alvarado (Anthropology, 2021), Jessica F. Brinkworth (Anthropology, PI), Luis Barreiro (University of Chicago, Co-PI)
Instrument: Zeiss LSM 700 four laser scanning confocal microscope, at Carl R. Woese Institute for Genomic Biology


Image showing Polymorphic Crystals of Human Kidney Stone featured in the New York Times published in a Scientific Reports manuscript. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-018-31890-9
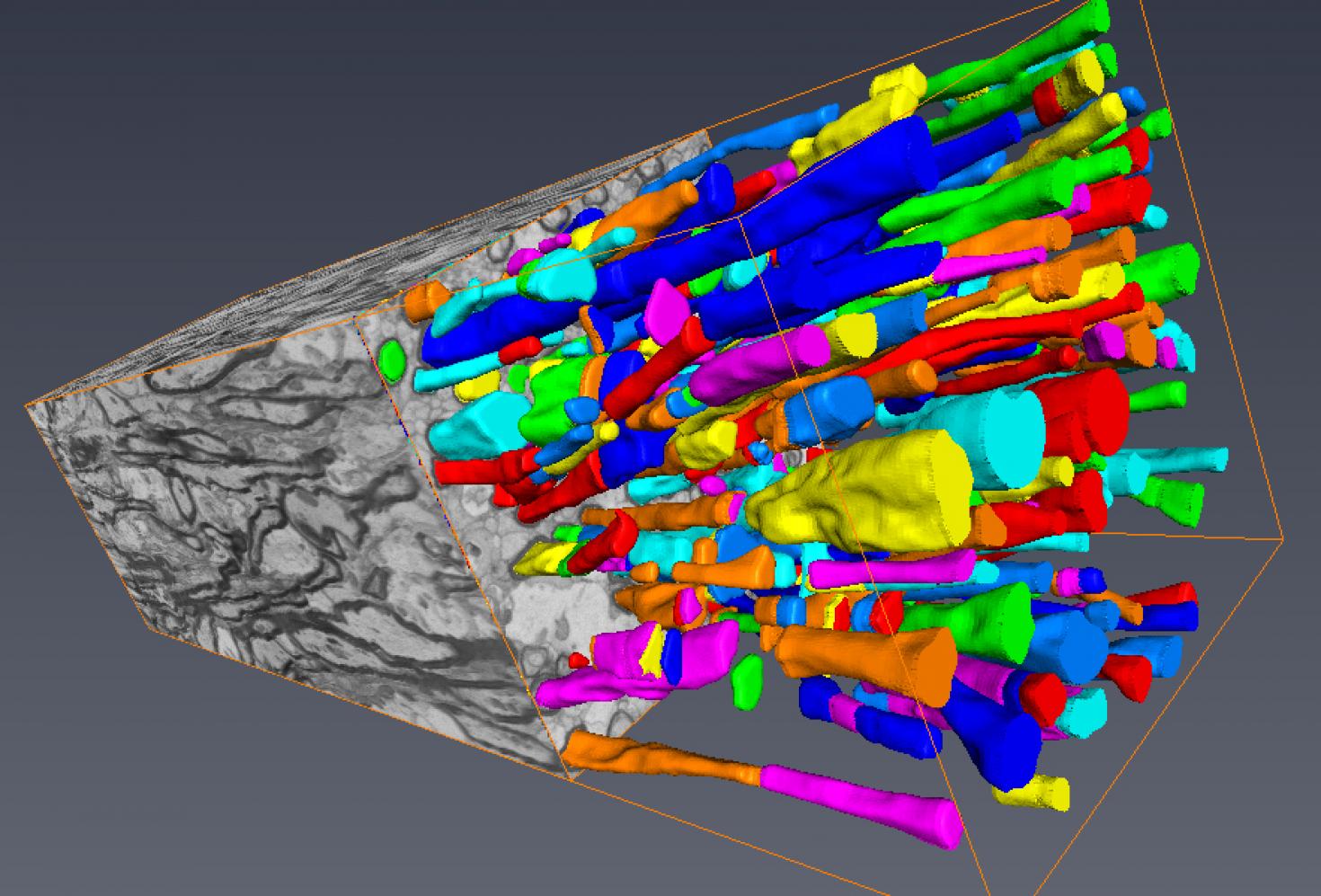

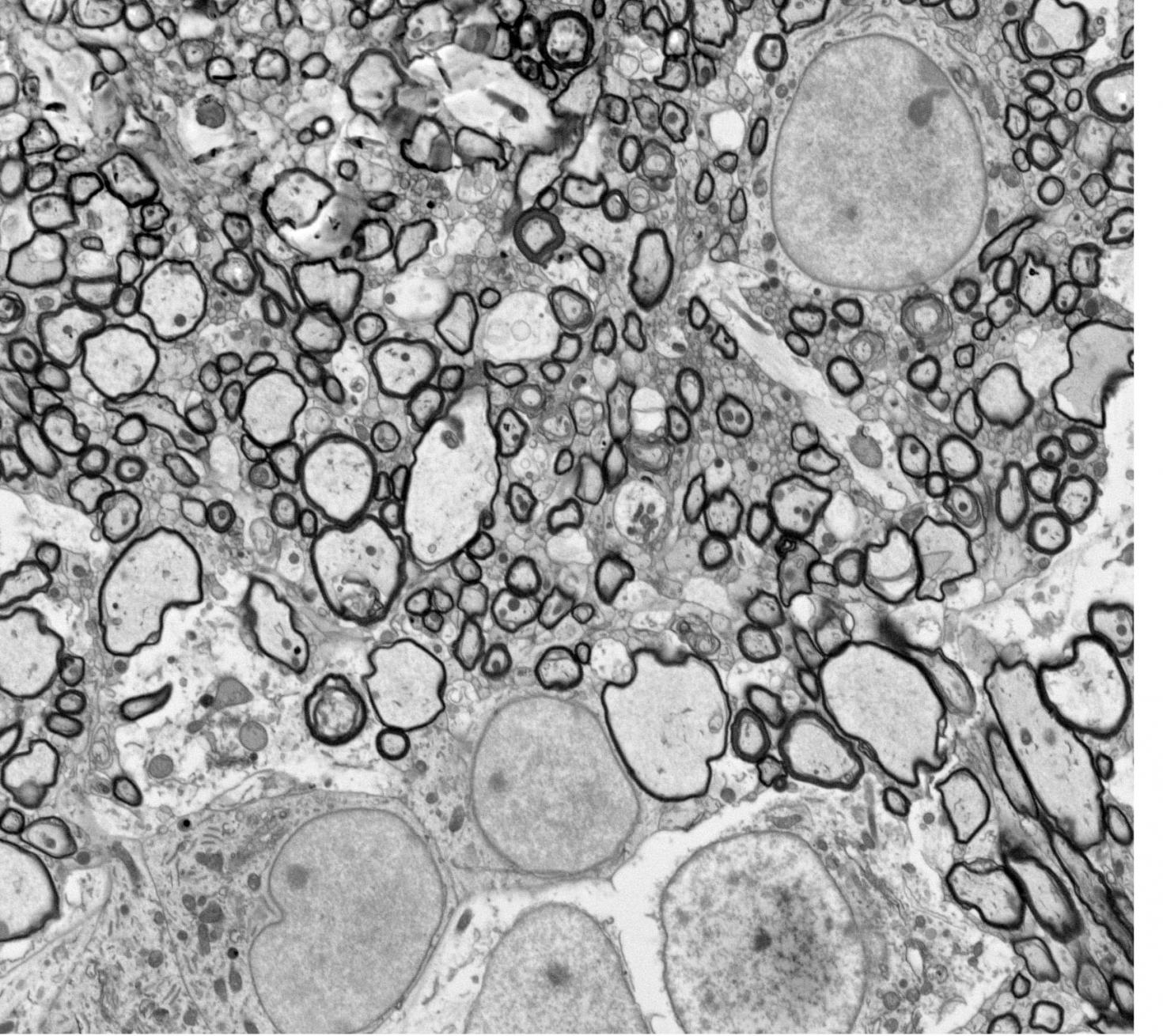
Segmented "Section of piglet corpus callosum" processed using serial block-face scanning electron microscopy. Myelinated axons are depicted by the dark circular rings. Image was acquired using the Zeiss Sigma BP 3View SBF-SEM and segmented using Amira Software.

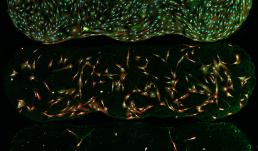


Hippocampal neurons cultured on a substrate immobilized with a cell adhesion molecule called N-cadherin as seen on the LSM 700. The green color represents microtubule-associated protein 2 (MAP2), a marker for neurons. The red color represents glial fibrillary acidic protein, a marker for glia. The blue color is DAPI staining of the nuclei. The picture is taken on the Zeiss LSM 700 confocal microscope.
The images show that neurons exhibit high levels of branching, neurite extensions, and neural connectivity when they are cultured on N-cadherin based substrates. In addition, the substrate also adheres glial cells, which are non-neuronal cells that support neuronal function. Together, this platform is useful for the generation of neurons for the fundamental studies of neuronal diseases and development, and can potentially be used to replace and repair diseased or damaged neurons in the brain.


A cross section of mouse testis showing germ cells and spermatogenesis. The green color is basigin expression, which is a cell membrane protein. The red color is claudin-4 expression, which is an epithelial tight junction protein. The blue color is DAPI staining of nuclei. The picture is taken on confocal microscope Zeiss LSM 710. The tubule structures are seminiferous tubules, and that is where spermatogenesis occurs. In each seminiferous tubule, there are 4-6 layers of germs cells at different developmental stages. In the lumen, the bright green color represents the tails of spermatozoa. The red colors in the lumen represent mature spermatozoa. The interstitial cells between each seminiferous tubule are Leydig cells and they produce male sex hormone testosterone, which is essential for normal spermatogenesis and maintaining male characteristics.

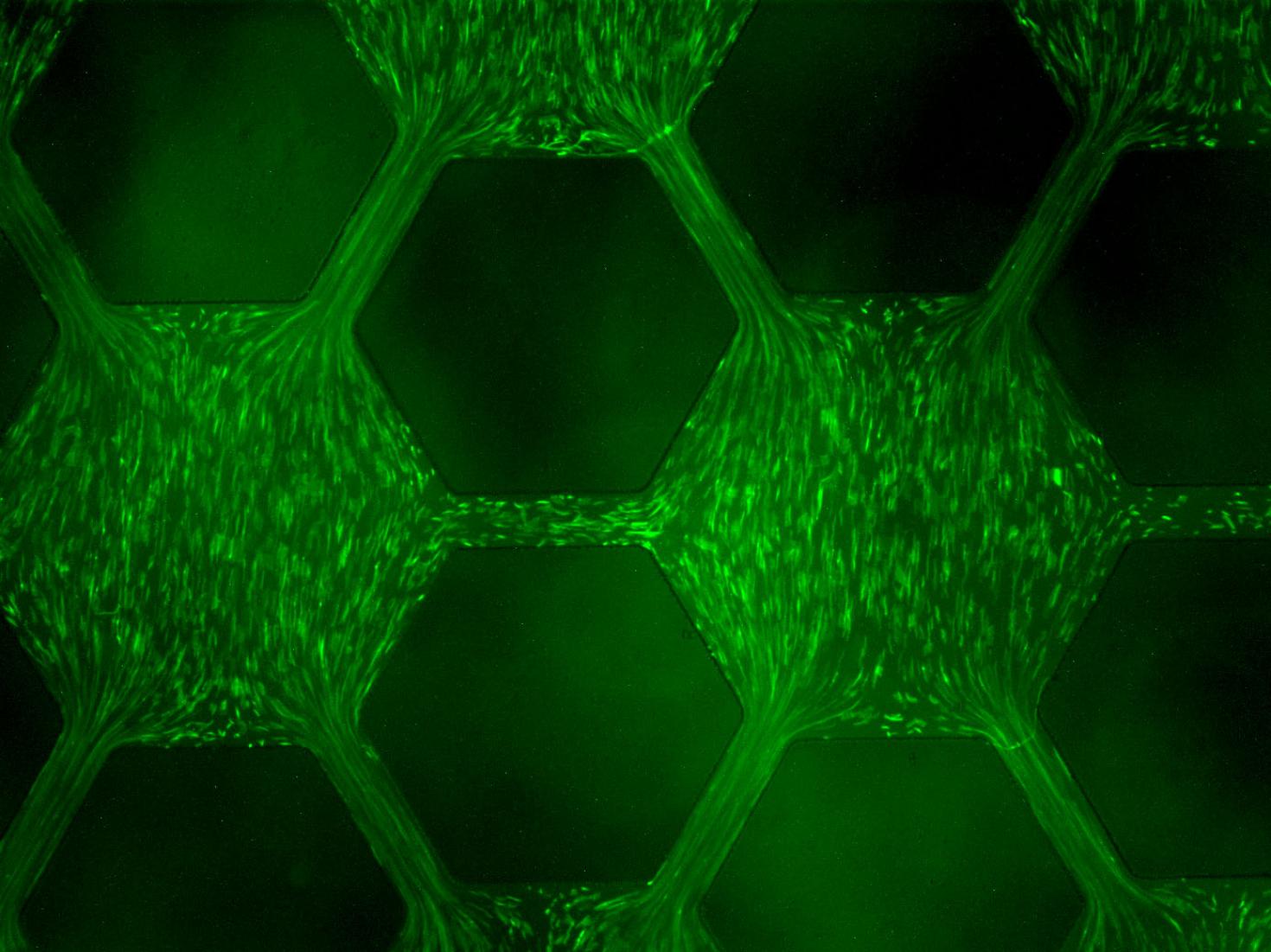

A microfluidic gradient chamber (MGC) was used to study the effects of different exposure histories on the development of resistance in bacteria in a porous network. An array of micro-scale hexagon wells interconnected with channels was built into the MGC to emulate a porous network. A linear concentration gradient of antibiotic ciprofloxacin was created across the well array, where E. coli cells with GFP were inoculate. Response of E. coli cells in the ciprofloxacin concentration gradient was observed in real-time.

View Gallery
1
/
10
